Endodontics is a pivotal branch of dentistry, often misunderstood but indispensable for preserving natural teeth. By exploring its basics step by step, both patients and practitioners can better appreciate its significance in maintaining oral health.
Table of Content
Understanding the Basic in Endodontics Step by Step
- What is Endodontics
- The Structure of a Tooth
- Common Endodontic Problems
- Key Tools and Instruments in Endodontics
- Understanding the Endodontic Diagnosis
- Step-by-Step Guide to Root Canal Treatment
- Techniques for Successful Root Canal Therapy
- Pain Management in Endodontics
- Common Challenges in Endodontics
- Advancements in Endodontic Technology
- The Role of Microscopes in Endodontics
- Preventive Endodontics
- Post-Treatment Care and Follow-Up
- Endodontic Emergencies and Their Management
- Myths About Endodontics
- The Future of Endodontics
- How to Choose an Endodontist
What is Endodontics
Defining Endodontics and Its Role in Dentistry
Endodontics specializes in diagnosing, preventing, and treating issues related to the dental pulp and periapical tissues. The primary goal is to save natural teeth by addressing conditions like deep decay, infections, or trauma. Root canal therapy is its hallmark procedure, aimed at eliminating pain while restoring functionality.
Why Understanding the Basics in Endodontics is Essential
Understanding the foundational principles of endodontics ensures that treatments are approached with clarity and precision. For patients, it alleviates fears and fosters trust. For professionals, it lays the groundwork for successful outcomes.
The Structure of a Tooth
Anatomy of the Tooth: Layers and Functions
A tooth consists of enamel, dentin, and pulp. The enamel is the protective outer layer, dentin provides support and sensitivity, and the pulp houses nerves and blood vessels essential for tooth vitality.
The Pulp Chamber and Its Importance in Endodontics
The pulp chamber is the core of the tooth, playing a critical role in development and sensation. When this area becomes inflamed or infected, endodontic intervention is necessary to alleviate pain and prevent further damage.
Common Endodontic Problems
Tooth Decay and Its Progression to the Pulp
Tooth decay begins on the surface but can penetrate deeper if untreated, eventually reaching the pulp. This progression leads to inflammation, pain, and potential abscesses.
Cracked or Fractured Teeth: An Endodontic Perspective
Cracks or fractures can expose the pulp to bacteria, causing infections that may necessitate root canal therapy. Early detection and treatment are crucial.
Traumatic Injuries Requiring Endodontic Care
Blunt force trauma to teeth can damage the pulp, even if the tooth remains intact. Endodontic treatments help restore these teeth to full functionality.
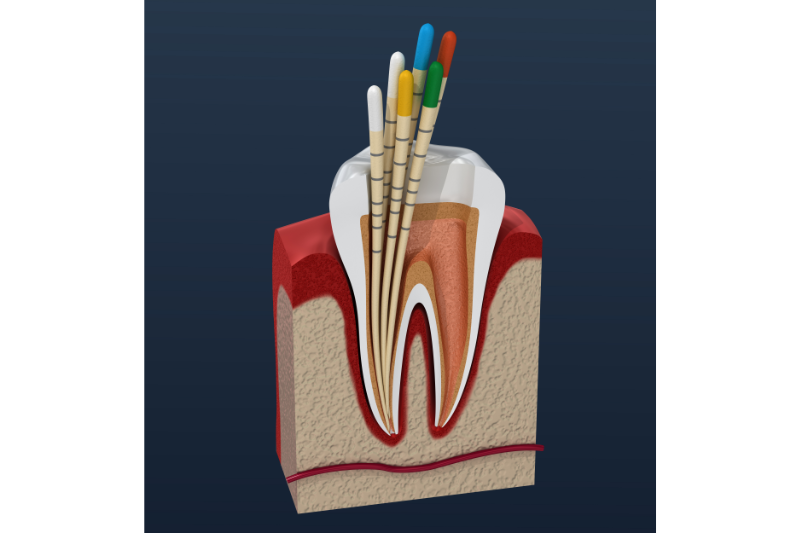
Key Tools and Instruments in Endodontics
Essential Hand Instruments for Root Canal Therapy
Files, explorers, and spreaders are vital hand tools used to navigate, clean, and shape root canals with precision.
The Role of Rotary Systems in Modern Endodontics
Rotary instruments, powered by electric or air-driven motors, streamline canal shaping and cleaning, ensuring efficiency and consistency.
Importance of Imaging Tools in Diagnosing Endodontic Issues
X-rays and advanced imaging like CBCT scans provide detailed insights into root canal anatomy, aiding in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Understanding the Endodontic Diagnosis
Recognizing Symptoms of Pulpal and Periapical Disease
Pain, sensitivity, swelling, and discoloration are common symptoms indicating pulpal or periapical issues requiring endodontic care.
The Importance of Radiographs in Endodontic Evaluation
Radiographs reveal hidden decay, root fractures, and infections, serving as an indispensable diagnostic tool for endodontists.
Differentiating Between Reversible and Irreversible Pulpitis
Reversible pulpitis can heal with timely treatment, while irreversible pulpitis necessitates root canal therapy to remove the affected pulp.
Step-by-Step Guide to Root Canal Treatment
Preparing for the Procedure: Patient Assessment and Setup
A comprehensive evaluation, including medical history and imaging, sets the stage for a successful root canal procedure.
Access Cavity Preparation: Finding the Pulp Chamber
Creating an access cavity allows the practitioner to locate the pulp chamber and canals, the first step in treatment.
Cleaning and Shaping the Root Canals: A Systematic Approach
Using files and irrigation, the canals are meticulously cleaned and shaped to remove debris and prepare for filling.
Irrigation Protocols for Effective Canal Disinfection
Antimicrobial solutions like sodium hypochlorite play a crucial role in eliminating bacteria and ensuring canal cleanliness.
Obturation: Filling the Canals to Seal the Tooth
The final step involves sealing the canals with materials like gutta-percha to prevent reinfection and restore the tooth.
Techniques for Successful Root Canal Therapy
The Role of Apex Locators in Determining Canal Length
Apex locators provide precise measurements of canal length, ensuring complete cleaning and obturation.
Effective Use of Sealers in Canal Filling
Dental sealers complement gutta-percha by filling microscopic spaces, creating a hermetic seal.
Managing Curved or Complex Canals
Advanced tools and techniques, like rotary systems and flexible files, enable effective treatment of challenging canal anatomies.
Pain Management in Endodontics
Local Anesthesia Techniques for Root Canal Procedures
Anesthesia ensures a pain-free experience, with techniques tailored to patient needs and the complexity of the case.
Managing Post-Treatment Discomfort and Complications
Post-treatment discomfort is typically mild and manageable with over-the-counter medications and aftercare instructions.
Common Challenges in Endodontics
Dealing with Calcified Canals
Calcifications can obstruct canal pathways, requiring specialized tools and techniques to navigate and treat effectively.
Managing Instrument Breakage During Treatment
Broken instruments can complicate treatment, but advanced retrieval methods often resolve the issue without compromising outcomes.
Handling Persistent Infections and Retreatment Cases
Persistent infections may require retreatment, necessitating meticulous cleaning and additional sealing efforts.
Advancements in Endodontic Technology
3D Imaging and Its Impact on Diagnosis and Treatment Planning
3D imaging provides unparalleled views of root canal systems, enabling precise diagnosis and customized treatments.
The Role of Lasers in Modern Endodontics
Lasers enhance disinfection and precision, improving treatment efficacy and reducing recovery time.
Bioceramic Materials for Enhanced Sealing
Bioceramics offer superior sealing properties, promoting healing and preventing reinfection.
The Role of Microscopes in Endodontics
Enhancing Precision and Visibility During Procedures
Microscopes allow for magnified views of canals, aiding in accurate diagnosis and precise treatment.
How Microscopy Improves Patient Outcomes
By enabling better visualization, microscopes reduce errors and improve the long-term success of root canal treatments.
Preventive Endodontics
Early Detection of Pulpal Issues Through Regular Checkups
Routine dental visits catch problems early, preventing the need for extensive treatments.
The Role of Sealants and Fluoride in Reducing Root Canal Needs
Preventive measures like sealants and fluoride applications protect teeth from decay, reducing the likelihood of pulp damage.
Post-Treatment Care and Follow-Up
Restoring the Tooth After a Root Canal: Crowns and Fillings
A crown or filling restores the tooth’s structure and function, ensuring durability and protection.
Long-Term Maintenance of Endodontically Treated Teeth
Good oral hygiene, regular dental visits, and avoiding hard foods prolong the life of treated teeth.
Endodontic Emergencies and Their Management
Handling Acute Pain and Swelling Before Treatment
Timely intervention with antibiotics and pain management stabilizes emergencies before definitive treatment.
Managing Flare-Ups During or After Root Canal Therapy
Effective communication and tailored care plans help manage rare but possible flare-ups post-treatment.
Myths About Endodontics
Debunking Misconceptions About Root Canals Being Painful
Modern techniques and anesthesia ensure root canals are virtually pain-free, contrary to popular belief.
Addressing Fears About Tooth Strength After Treatment
Proper restoration ensures treated teeth remain strong and functional for years.
The Future of Endodontics
Artificial Intelligence in Diagnosis and Treatment Planning
AI-driven tools enhance diagnostic accuracy and streamline treatment planning for better outcomes.
Regenerative Endodontics: The Potential of Pulp Regeneration
Advances in stem cell research offer hope for regenerating natural pulp tissue, revolutionizing endodontic care.
How to Choose an Endodontist
The Importance of Specialist Care for Complex Cases
Endodontists have advanced training, making them the best choice for intricate root canal treatments.
Questions to Ask Before Starting Treatment
Discussing experience, techniques, and expected outcomes ensures informed decisions and peace of mind.
Endodontics is a vital field that preserves natural teeth and enhances oral health. Understanding its basics empowers patients and professionals alike to make informed decisions, ensuring successful treatments and lifelong benefits.
Recent Blogs
Stay Updated With Our Latest Blogs
Be the first to know! Subscribe for fresh content, exclusive insights, and fuel your knowledge now!